特别声明:本内容由AI生成,作者自己做并检查了一遍,请谨慎参考!
Computer Networks Final Exam
Total Points: 100
Instructions: Please answer all questions in the following sections.
Part I: Multiple Choice (15 points)
(Instructions: Select the best answer for each question. Each question is worth 1 point.)
What is the primary purpose of adding a header to data at each layer of the protocol stack? B
To increase the size of the message
To add control information for that layer’s function
To encrypt the data for security
To compress the data for efficiency
If a system has an n-layer protocol hierarchy and adds an h-byte header at each layer to an M-byte application message, what is the fraction of network bandwidth filled with headers? C
M/(M+n⋅h)
(n⋅h)/M
(n⋅h)/(M+n⋅h)
M/(n⋅h)
In a lightly loaded packet-switched network, the total delay for an x-bit message over a k-hop path is primarily determined by: A
The sum of transmission delays at each hop and the total propagation delay.
Only the circuit setup time.
The number of hops multiplied by the propagation delay per hop.
The message size divided by the number of packets.
A key parameter for characterizing the Quality of Service (QoS) for digitized voice and video traffic, besides bandwidth and latency, is: B
Packet survival time
Jitter (variation in packet delay)
Throughput
Error rate
Which of the following is a primary characteristic of connection-oriented communication?
It sends data without establishing a prior connection.
It guarantees data will arrive in the order it was sent.
It is best used for real-time streaming.
It has lower overhead than connectionless communication.
In the context of CRC error detection, why is the CRC placed in the trailer instead of the header?
To make the header smaller.
To allow the hardware to calculate the checksum while the frame is being transmitted.
To comply with the OSI model.
To make error correction easier.
For a CSMA/CD network, what is the critical relationship between minimum frame size and the network’s characteristics?
The minimum frame size must be smaller than the cable length.
The transmission time for the minimum frame size must be at least twice the propagation delay (2τ).
The baud rate must be twice the data rate.
The minimum frame size is always 64 bytes, regardless of network speed or length.
What happens when a VLAN-aware switch receives a frame from a legacy (non-VLAN) device that needs to be sent across a VLAN trunk?
The frame is discarded.
The frame is forwarded without modification.
The switch adds the appropriate VLAN tag to the frame.
The switch sends a request to the source device to add a tag.
What is the primary reason the IPv4 ‘Protocol’ field was not included in the main IPv6 header?
It was deemed unnecessary for modern networking.
Its function is handled by the ‘Next Header’ field in IPv6.
IPv6 does not support different transport layer protocols.
To reduce the header size to be smaller than IPv4’s.
What is the maximum number of hosts a network with the subnet mask 255.255.240.0 can support?
4096
4094
2048
2046
What is the main advantage of a store-and-forward switch over a cut-through switch regarding frame errors?
Store-and-forward switches have lower latency.
Store-and-forward switches can check the entire frame for CRC errors before forwarding.
Cut-through switches cannot handle damaged frames at all.
Store-and-forward switches can correct damaged frames automatically.
In the TCP slow start algorithm, if the current congestion window is 4 KB, and the sender receives acknowledgements for all segments, what will the new congestion window size be?
5 KB
6 KB
8 KB
16 KB
A DNS name lookup for a name that is longer than the maximum UDP packet size will:
Be split into two UDP packets.
Fail, as UDP will not send the packet.
Automatically switch to TCP.
Be truncated to fit the maximum size.
The principal difference between POP3 and IMAP is:
POP3 is more secure than IMAP.
IMAP allows the user to manage emails directly on the server, while POP3 downloads them.
Only POP3 can be used with webmail.
IMAP is an older, obsolete protocol.
What is the baud rate of the classic 10-Mbps Ethernet that uses Manchester encoding?
10 Mbaud
5 Mbaud
20 Mbaud
1 Mbaud
Part II: True or False (15 points)
(Instructions: Mark ‘T’ for true or ‘F’ for false for each statement. Each question is worth 1 point.)
- ( T / F ) A possible disadvantage
of layered protocols is that the performance can be worse than in a
non-layered system due to header and processing overhead.
- ( T / F ) UDP (User Datagram
Protocol) is an example of a connection-oriented protocol.
- ( T / F ) In network protocols, a
frame encapsulates a packet.
- ( T / F ) The Nyquist theorem
applies only to copper wire and not to optical fiber.
- ( T / F ) A modem constellation
diagram with data points only at (0, 1) and (0, 2) is using phase
modulation.
- ( T / F ) The purpose of byte
stuffing in a data link protocol is to handle accidental flag bytes
within the payload.
- ( T / F ) In a Go-Back-N ARQ
protocol, if an acknowledgment for frame 5 is received, it implies that
frames 0 through 5 have all been received correctly by the
receiver.
- ( T / F ) Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps)
maintains the same 64-byte minimum frame size as 10-Mbps Ethernet by
increasing the maximum allowed cable length.
- ( T / F ) A standard network hub
requires a configuration table to support Virtual LANs (VLANs).
- ( T / F ) With Distance Vector
Routing, a router’s new routing table is calculated based only on the
vectors received from its neighbors and its own costs to those
neighbors, ignoring its old table.
- ( T / F ) The IP checksum covers
both the IP header and the data payload to ensure end-to-end data
integrity.
- ( T / F ) A single DNS name can be
associated with multiple IP addresses.
- ( T / F ) When a TCP timeout
occurs, the congestion window is reset to half of its previous
value.
- ( T / F ) Webmail services like
Gmail or Outlook.com use HTTP for communication between the user’s
browser and the mail server, but the spirit of operation is closer to
IMAP than POP3.
- ( T / F ) In a packet-switched network, it is impossible for packets to be delivered out of order.
Part III: Fill in the Blanks (20 points)
(Instructions: Complete the following statements. Each question is worth 2 points.)
- The two main reasons for using layered protocols are to simplify
design and implementation, and to ensure that modifications in one layer
do not affect other layers as long as the __________ are
unchanged.
- If 10 signals, each requiring 4000 Hz, are multiplexed using FDM
with 400 Hz guard bands, the minimum required bandwidth for the channel
is __________ Hz.
- For a channel with a 4 kbps bit rate and 20 msec propagation delay,
a stop-and-wait protocol achieves at least 50% efficiency if the frame
size is at least __________ bits.
- A 100-km-long cable with a T1 data rate (1.544 Mbps) and a
propagation speed of 2/3 the speed of light can hold __________
bits.
- The fraction of slots wasted due to collisions in a slotted
ALOHA-like system with n hosts each transmitting with probability p is
given by the formula __________.
- For a 1 Gbps CSMA/CD network over a 1-km cable where the signal
speed is 200,000 km/sec, the minimum frame size must be __________
bits.
- A router receiving CIDR address blocks 57.6.96.0/21, 57.6.104.0/21,
57.6.112.0/21, and 57.6.120.0/21 for the same outgoing line can
aggregate them into the single block __________.
- The primary function that UDP provides on top of raw IP is
__________ to allow for process-to-process communication.
- A TCP machine sending 65,535-byte windows over a 1-Gbps channel with
a 10-msec one-way delay achieves a maximum throughput of __________
Mbps.
- After a TCP timeout, the congestion control algorithm sets the slow start threshold to half the current window size and resets the congestion window to __________.
Part IV: Short Answer and Calculation (40 points)
(Instructions: Answer the following questions. Show your calculations where necessary. Point values are indicated for each question.)
(8 points) An upper-layer packet is split into 10 frames. Each frame has an 80% chance of arriving undamaged. If the data link layer performs no error control, how many times must the message be sent on average to get the entire message through?
(8 points) A datagram network allows routers to drop packets with a probability p. A source host is connected to a source router, which is connected to a destination router, and then to the destination host1 (a 3-hop path). If a packet is dropped by either router, the source host times out and retransmits.
What is the probability that a single transmission is successful?
What is the mean number of transmissions required to get the packet delivered?
(8 points) A TCP flow has a maximum packet size of 1000 bytes, a token bucket rate of 10 million bytes/sec, and a token bucket size (B) of 1 million bytes. The maximum transmission rate (M) is 50 million bytes/sec. For how long can the flow sustain a burst at the maximum transmission rate?
(8 points) Four organizations (A, B, C, D) request IP addresses from a large block starting at 198.16.0.0. The requests are for 4000, 2000, 4000, and 8000 addresses, respectively, and are fulfilled in that order. For organization C, provide:
The number of addresses that will be allocated.
The first IP address assigned.
The last IP address assigned.
The network mask in CIDR notation (e.g., /s).
(8 points) Consider a TCP connection using the slow start algorithm on a line with a 10 msec round-trip time and no congestion. The receiver’s window is 24 KB, and the maximum segment size (MSS) is 2 KB. How long does it take before the sender can send a full 24 KB window? Show the state of the congestion window at each step (RTT).
Part V: Protocol Analysis (10 points)
(Instructions: Analyze the following scenario and answer the questions.)
A TCP message containing 900 bytes of data and a 20-byte TCP header is sent from Host A to Host B. The path is A -> R1 -> R2 -> B. The IP header is 20 bytes. The links have the following Maximum Transmission Units (MTUs) for the entire frame:
- Link A-R1: MTU = 1024 bytes (frame header = 14
bytes)
- Link R1-R2: MTU = 512 bytes (frame header = 8
bytes)
- Link R2-B: MTU = 512 bytes (frame header = 12 bytes)
The IP datagram must be fragmented at router R1 to cross the R1-R2 link. Assume the original IP datagram has an Identification value of 555.
Describe the IP fragments that are transmitted from R1 to R2. For each fragment, specify the following fields from its IP header:
- Total Length
- Identification
- More Fragments (MF) bit
- Fragment Offset
ANSWER KEY
Part I: Multiple Choice (15 points)
b) To add control information for that layer’s function 2222
c) (n⋅h)/(M+n⋅h) 3333
a) The sum of transmission delays at each hop and the total propagation delay. 4444
b) Jitter (variation in packet delay) 5555
b) It guarantees data will arrive in the order it was sent. 6666
b) To allow the hardware to calculate the checksum while the frame is being transmitted. 7777
b) The transmission time for the minimum frame size must be at least twice the propagation delay (2τ). 8888
c) The switch adds the appropriate VLAN tag to the frame. 9999
b) Its function is handled by the ‘Next Header’ field in IPv6. 10101010
b) 4094 11
b) Store-and-forward switches can check the entire frame for CRC errors before forwarding. 12121212
c) 8 KB 13131313
b) Fail, as UDP will not send the packet. 14141414
b) IMAP allows the user to manage emails directly on the server, while POP3 downloads them. 15151515151515151515151515151515
c) 20 Mbaud 16161616
Part II: True or False (15 points)
T 17171717
F (UDP is connectionless) 18181818
T 19191919
F (It’s a mathematical property applicable to any medium) 20202020
F (This is amplitude modulation, as phase is constant but amplitude changes) 21212121
T 22222222
T (This describes cumulative acknowledgment in GBN) 23232323
F (It achieves this by reducing the maximum cable length) 24242424
F (Hubs are physical layer devices and not VLAN-aware) 25252525
T 26262626
F (The IP checksum only covers the header) 27272727
T 28282828
F (It resets to 1 MSS) 29292929
T 30303030
F (Packets can be rerouted and arrive out of order, which is why TCP needs sequence numbers) 31313131
Part III: Fill in the Blanks (20 points)
services and interfaces 32323232
43,600 33
160 34343434
772 35353535
1−n⋅p⋅(1−p)n−1−(1−p)n 36363636
10,000 37373737
57.6.96.0/19 38
port numbers (or multiplexing/demultiplexing) 39393939
26.214 40404040
1 MSS (Maximum Segment Size) 41414141
Part IV: Short Answer and Calculation (40 points)
Answer:
The probability of a single frame arriving successfully is 0.8.
The probability of all 10 frames arriving successfully in one transmission is Psuccess=(0.8)10≈0.10742424242.
The mean number of transmissions is a geometric distribution, given by 1/Psuccess.
Mean number of transmissions = 1/0.107≈9.3 times43434343.
Answer:
The probability of a router not dropping a packet is (1−p).
For a successful transmission, the packet must pass through both routers. The probability is Psuccess=(1−p)⋅(1−p)=(1−p)244444444.
This is another geometric distribution. The mean number of transmissions is 1/Psuccess.
Mean number of transmissions = 1/(1−p)245454545.
Answer:
The formula for the duration of a burst (S) at maximum speed is S=B/(M−R), where B is the bucket size, M is the max rate, and R is the token rate46464646.
- B = 1,000,000 bytes
- M = 50,000,000 bytes/sec
- R = 10,000,000 bytes/sec S=1,000,000/(50,000,000−10,000,000)=1,000,000/40,000,000=0.025 seconds. The burst can last for 25 milliseconds47474747.
- B = 1,000,000 bytes
Answer:
- A needs 4000 addresses -> allocate 212=4096. Range: 198.16.0.0 to
198.16.15.255 (/20).
- B needs 2000 addresses -> allocate 211=2048. Range: 198.16.16.0
to 198.16.23.255 (/21).
- The next available address is 198.16.24.0. However, C needs 4000 addresses (block size 4096), which must start on a boundary divisible by the block size. The next such boundary after 198.16.23.255 is 198.16.32.0.
For organization C:
Allocated addresses: 409648484848.
First IP: 198.16.32.049494949.
Last IP: 198.16.47.25550505050.
Mask: /2051515151.
- A needs 4000 addresses -> allocate 212=4096. Range: 198.16.0.0 to
198.16.15.255 (/20).
Answer:
The receive window is 24 KB and MSS is 2 KB. The congestion window (cwnd) starts at 1 MSS (2 KB) and doubles each RTT until it reaches the slow start threshold52525252. The sending window is min(cwnd, receive window).
- t=0: Send 1 segment. cwnd = 2 KB.
- t=1 RTT (10ms): ACK received. cwnd = 2 * 2KB = 4
KB. Send 2 segments.
- t=2 RTT (20ms): ACKs received. cwnd = 2 * 4KB = 8
KB. Send 4 segments.
- t=3 RTT (30ms): ACKs received. cwnd = 2 * 8KB = 16
KB. Send 8 segments.
- t=4 RTT (40ms): ACKs received. cwnd = 2 * 16KB = 32 KB. At this point, the sending window = min(cwnd=32KB, recv_win=24KB) = 24 KB. It takes 4 RTTs, or 40 msec, to send a full window53535353.
- t=0: Send 1 segment. cwnd = 2 KB.
Part V: Protocol Analysis (10 points)
Analysis:
Initial Datagram: The total data payload for the IP datagram is 900 (TCP data) + 20 (TCP header) = 920 bytes. With a 20-byte IP header, the total IP datagram length is 940 bytes54545454.
MTU Calculation:
- Link A-R1 IP MTU = 1024 - 14 = 1010 bytes. The 940-byte datagram
passes without fragmentation.
- Link R1-R2 IP MTU = 512 - 8 = 504 bytes. The 940-byte datagram must
be fragmented.
- Link A-R1 IP MTU = 1024 - 14 = 1010 bytes. The 940-byte datagram
passes without fragmentation.
Fragmentation Logic: The data portion of each fragment must be a multiple of 8 bytes (except for the last one).
- Max data in first fragment = 504 (IP MTU) - 20 (IP Header) = 484
bytes. The largest multiple of 8 less than or equal to 484 is 480
bytes.
- Fragment 1: Data = 480 bytes. Total Length = 480 +
20 = 500 bytes.
- Remaining Data: 920 - 480 = 440 bytes.
- Fragment 2: Data = 440 bytes. Total Length = 440 + 20 = 460 bytes.
- Max data in first fragment = 504 (IP MTU) - 20 (IP Header) = 484
bytes. The largest multiple of 8 less than or equal to 484 is 480
bytes.
Answer:
The two fragments transmitted from R1 to R2 are55555555:
Fragment 1:
- Total Length: 500
- Identification: 555
- More Fragments (MF) bit: 1 (true)
- Fragment Offset: 0
Fragment 2:
- Total Length: 460
- Identification: 555
- More Fragments (MF) bit: 0 (false)
- Fragment Offset: 60 (The offset is the data from the previous fragment(s) divided by 8: 480 / 8 = 60) 56565656
附录1:IP报头格式
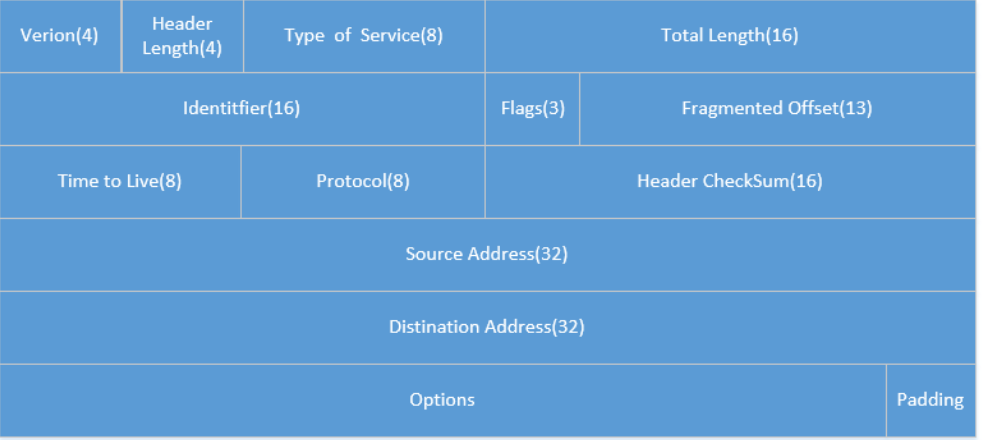
Protocol 域为1, 6, 17, 89分别对应 ICMP, TCP, UDP, OSPF 协议。
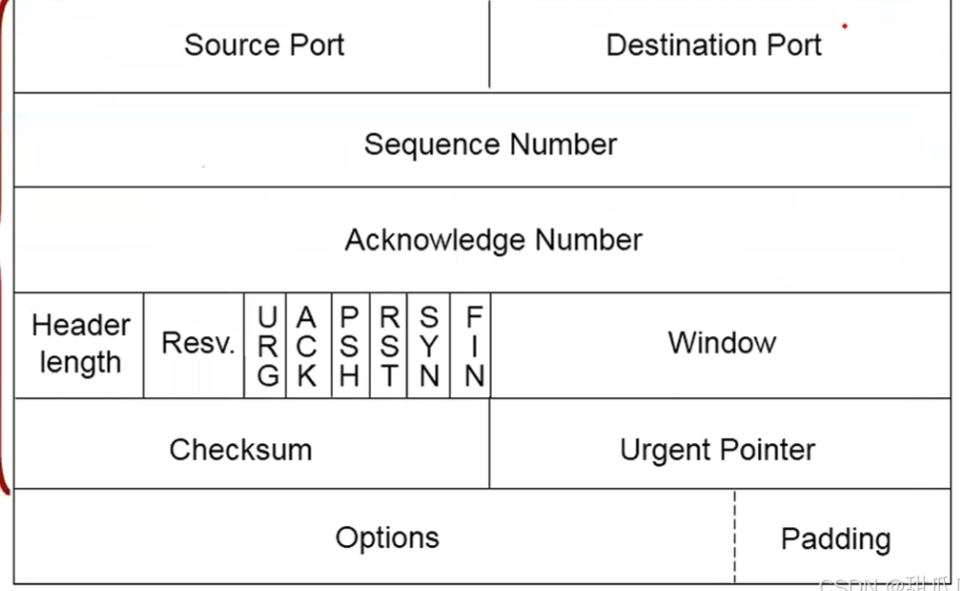
附录2:TCP 报头格式 (Window size
域描述窗口时使用的计量单位为1字节, MSS值为1460)
如果您喜欢我的文章,可以考虑打赏以支持我继续创作.




